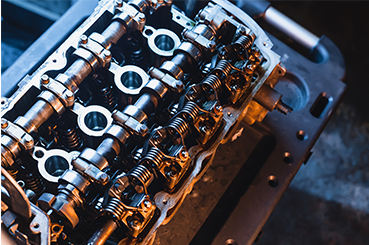
Your car engine is a complex network of parts working together in perfect harmony.
Today, we’re focusing on the cylinder head, a crucial component that plays a starring role in generating the power that gets your car moving.
Buckle up and get ready to learn some interesting facts that will turn you into an instant cylinder head connoisseur!
What is a cylinder head?
The cylinder head, often simply called the “head,” sits on top of the engine block like a well-fitting lid. It forms the roof of the combustion chamber, where the magic happens – fuel is burned in a controlled explosion to create the force that drives the pistons up and down.
What are cylinder heads, and what are their functions?
Cylinder heads are like the control centre of the combustion process, acting as a stage for several key players:
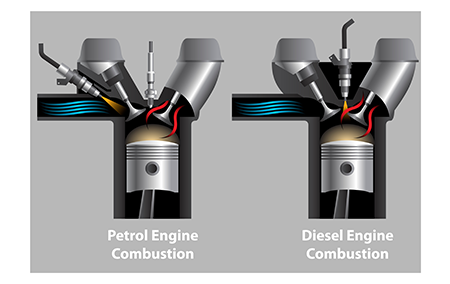
- Intake and exhaust ports: These channels are the intake and exhaust highways of the engine. The intake ports are the entry points for the air-fuel mixture, while the exhaust ports are the exit route for the leftover gases after the combustion party.
- Valves: Imagine these as bouncers controlling the flow of traffic through the ports. Opened and closed by the camshaft, the intake valves usher in the fresh air-fuel mixture, while the exhaust valves show the spent gases at the door.
- Spark plugs (petrol engines) or glow plugs (diesel engines): These are essentially the igniters of the engine. In petrol engines, spark plugs create a spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture, triggering the combustion process. Glow plugs in diesel engines heat up the air in the cylinder to aid the combustion of the fuel.
- Coolant passages: The engine burns hot during operation, and these channels are the circulatory system for the engine coolant. The coolant absorbs the heat and carries it away to the radiator, where it is released and the cycle continues, keeping the engine from overheating.
In essence, the cylinder head manages the air and fuel intake, ignition, and temperature control – all working together like a well-rehearsed orchestra to create the smooth operation of your car engine.
Is the cylinder head the same as the head gasket?
No, the cylinder head and head gasket are two separate parts, but they work together in a crucial partnership.
The head gasket is a vital seal sandwiched between the cylinder head and the engine block. Imagine it as a high-pressure gasket that ensures a leak-proof connection.
Without this seal, oil, coolant, and combustion gases could leak and wreak havoc on the engine’s performance.
What does the number of cylinders in a car engine mean?
The number of cylinders refers to the number of separate combustion chambers within the engine. Each cylinder is like a miniature power plant, and the more cylinders you have, the more potential power you have at your disposal.
A 4-cylinder engine has four chambers, a 6-cylinder engine has six, and so on.
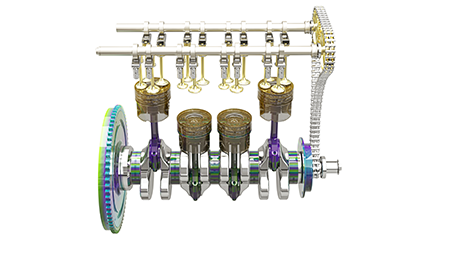
Generally, more cylinders translate to more power and potentially better acceleration. However, this also often means increased fuel consumption, as more cylinders require more fuel to be fed. So, it’s a bit of a balancing act between power and efficiency.
Is cylinder capacity engine size?
Cylinder capacity, also known as engine displacement, is often used as an indicator of engine size.
It’s typically measured in litres (L) and represents the total volume of all the cylinders in the engine. Imagine it as the total cubic capacity available for the pistons to move up and down. Broadly, a larger displacement engine, with more total volume, can pack a bigger punch and produce more power.
However, modern engine technology has introduced features like turbochargers that can force more air into the engine, influencing power output without relying solely on the size of the cylinders. So, while cylinder capacity is a good starting point to understand engine size and potential power, it’s not the whole story.
Where is the cylinder head located in an engine?
The cylinder head is situated on the top of the engine block, and unlike some internal engine parts, it’s a distinct component. Imagine the engine block as the base of the engine, and the cylinder head is like a securely bolted-on lid. This allows mechanics to detach the cylinder head for maintenance or repairs if needed.
What are common cylinder head problems?
While cylinder heads are generally durable and built to withstand the pressures of combustion, some common problems can arise:
Head gasket failure:
A faulty head gasket, like a worn-out washer, can cause leaks of oil, coolant, or combustion gases. This can lead to a range of symptoms, like engine overheating, rough idling, or unusual exhaust smoke.
Warped cylinder head:
Extreme engine overheating can warp the cylinder head, affecting the seal with the block and causing the same issues as a failing head gasket. Imagine the cylinder head as a flat surface that needs to perfectly match the engine block for a tight seal. If the head warps from overheating, it becomes uneven, compromising the seal and leading to potential leaks.
Valve problems:
The valves are constantly opening and closing under high temperatures, and over time they can wear out, bend, or develop carbon deposits. Worn or damaged valves can compromise sealing, leading to inefficient combustion, power loss, and rough engine idle.
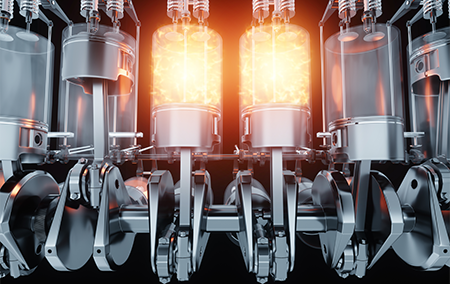
So, there you have it! We’ve explored the fascinating world of cylinder heads, from their role in the combustion process to their location within the engine.
Understanding this key component can help you appreciate the complex mechanics at work under the hood of your car. The next time you hear your engine purr, you’ll know it’s thanks in part to the intricate dance happening within the cylinder head, meticulously managing air, fuel, ignition, and temperature to propel you down the road.
If you’re ever curious about unusual engine noises or performance issues, remember the cylinder head and its potential problems. Consulting a mechanic for diagnosis and repair can ensure your cylinder head continues to be the maestro of your engine’s performance!